Clinical efficacy of lung transplantation for lung chronic graft-versus-host disease after hematopoietic stem cell transplantation
-
摘要:
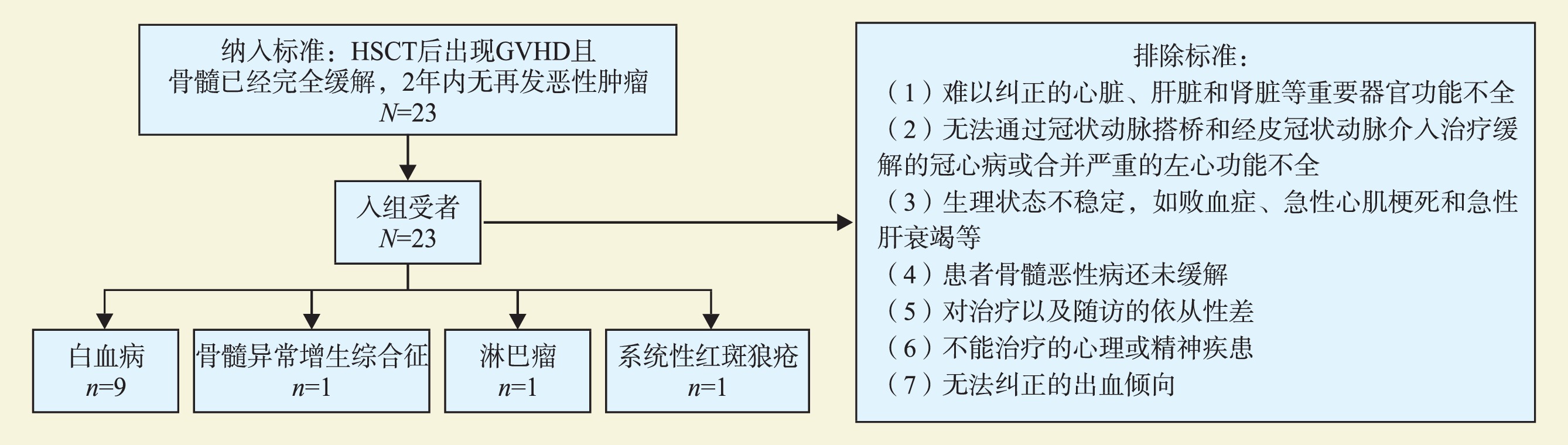
目的 探讨肺移植治疗造血干细胞移植(HSCT)后肺部慢性移植物抗宿主病(cGVHD)的疗效。 方法 回顾性分析因肺部cGVHD接受肺移植治疗的12例患者的临床资料。分析患者的术前临床表现及累及器官,对比肺移植前后肺功能,分析患者肺移植术后生存情况。 结果 11例患者因原发血液系统恶性疾病行HSCT,其中白血病9例、骨髓增生异常综合征1例、淋巴瘤1例,1例因系统性红斑狼疮行HSCT。12例cGVHD患者中,8例同时累及皮肤,5例同时累及口腔,4例同时累及胃肠道,3例同时累及肝脏。12例患者肺移植术前均存在严重肺部cGVHD导致的呼吸衰竭,其中表现为Ⅱ型呼吸衰竭9例;表现为Ⅰ型呼吸衰竭3例。肺移植手术方式包括右肺移植2例、左肺移植2例、双肺移植8例。从接受HSCT到接受肺移植的间隔时间为75(19~187)个月。截至投稿日,随访时间为18(7~74)个月,其中10例患者存活,1例于术后22个月死于重症肝炎,另外1例于术后6个月死于消化道大出血,存活患者均未发现原发病复发。 结论 肺移植是治疗HSCT后肺部cGVHD的一种有效手段,可延长患者生存时间并提高生活质量。 Abstract:Objective To evaluate clinical efficacy of lung transplantation for lung chronic graft-versus-host disease (cGVHD) after hematopoietic stem cell transplantation (HSCT). Methods Clinical data of 12 patients undergoing lung transplantation for lung cGVHD were retrospectively analyzed. Preoperative clinical manifestations and involved organs of patients were analyzed. The lung function before and after lung transplantation was compared, and the survival of patients after lung transplantation was analyzed. Results 11 patients underwent HSCT due to primary hematological malignancies, including 9 cases of leukemia, 1 case of myelodysplastic syndrome, 1 case of lymphoma. And 1 case underwent HSCT for systemic lupus erythematosus. Among 12 cGVHD patients, skin involvement was found in 8 cases, oral cavity involvement in 5 cases, gastrointestinal tract involvement in 4 cases and liver involvement in 3 cases. All 12 patients developed severe respiratory failure caused by cGVHD before lung transplantation, including 9 cases of typeⅡ respiratory failure and 3 cases of type Ⅰ respiratory failure. Two patients underwent right lung transplantation, 2 cases of left lung transplantation and 8 cases of bilateral lung transplantation. The interval from HSCT to lung transplantation was 75 (19-187) months. Upon the date of submission, postoperative follow-up time was 18 (7-74) months. Ten patients survived, 1 died from severe hepatitis at postoperative 22 months, and 1 died from gastrointestinal bleeding at postoperative 6 months. No recurrence of primary diseases was reported in surviving patients. Conclusions Lung transplantation is an efficacious treatment for lung cGVHD after HSCT, which may prolong the survival time and improve the quality of life of the recipients. -
表 1 12例接受肺移植患者的临床资料
Table 1. Clinical data of 12 patients receiving lung transplantation
例号 性别 年龄(岁) 术前BMI
(kg/m2)原发病 肺移植指征 HSCT日期 骨髓
配型累及器官 肺移植
日期术式 术后情况 现生存情况 6分钟步行试验(m) 1 男 20 16.4 ALL① BOS 2018年7月30日 全相合 肺、皮肤、口腔、肝脏、胃肠道 2020年3月19日 双肺移植 顺利出院 良好 404 2 女 35 15.8 AML② BOS 2006年6月 全相合 肺、皮肤、
肝脏2021年8月9日 双肺移植 顺利出院 良好 376 3 男 19 17.0 AML BOS 2018年3月29日 半相合 肺、肝脏 2021年8月14日 双肺移植 顺利出院 良好 650 4 女 37 11.7 MDS③ BOS 2017年6月 全相合 肺、眼睛 2021年11月23日 双肺移植 顺利出院 良好 460 5 女 39 14.8 ALL BOS 2014年7月 全相合 肺、口腔 2021年12月15日 双肺移植 顺利出院 良好 330 6 男 33 24.7 ALL BOS 2006年7月 全相合 肺、皮肤、口腔、胃肠道 2022年2月12日 双肺移植 顺利出院 良好 488 7 男 38 14.9 ALL BOS 2006年6月 全相合 肺、口腔 2022年2月9日 左肺移植 顺利出院 良好 325 8 男 39 13.9 AML ILD 2013年5月 全相合 肺、胃肠道、皮肤 2022年3月10日 右肺移植 顺利出院 术后6个月死亡 —④ 9 男 31 15.6 ALL BOS 2017年7月 全相合 肺、口腔、眼睛、皮肤 2022年10月16日 双肺移植 顺利出院 良好 480 10 女 42 14.1 ALL BOS 2019年7月26日 半相合 肺、眼睛、指甲、皮肤、胃肠道 2022年9月21日 双肺移植 顺利出院 良好 457 11 女 41 21.1 SLE ILD 2007年4月8日 半相合 肺、皮肤 2017年3月11日 右肺移植 顺利出院 良好 400 12 男 29 17.2 淋巴瘤 PPFE 2011年9月14日 半相合 肺、皮肤 2016年3月5日 左肺移植 顺利出院 术后22个月死亡 — 注:①ALL为急性淋巴细胞白血病。
②AML为急性髓系白血病。
③MDS为骨髓异常增生综合征。
④—为无数据。 -
[1] NIEDERWIESER D, BALDOMERO H, SZER J, et al. Hematopoietic stem cell transplantation activity worldwide in 2012 and a SWOT analysis of the Worldwide Network for Blood and Marrow Transplantation Group including the global survey[J]. Bone Marrow Transplant, 2016, 51(6): 778-785. DOI: 10.1038/bmt.2016.18. [2] BOLAÑOS-MEADE J, HAMADANI M, WU J, et al. Post-Transplantation cyclophosphamide-based graft-versus-host disease prophylaxis[J]. N Engl J Med, 2023, 388(25): 2338-2348. DOI: 10.1056/NEJMoa2215943. [3] XU L, CHEN H, CHEN J, et al. The consensus on indications, conditioning regimen, and donor selection of allogeneic hematopoietic cell transplantation for hematological diseases in China-recommendations from the Chinese Society of Hematology[J]. J Hematol Oncol, 2018, 11(1): 33. DOI: 10.1186/s13045-018-0564-x. [4] WANG Y, CHEN H, CHEN J, et al. The consensus on the monitoring, treatment, and prevention of leukemia relapse after allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation in China[J]. Cancer Lett, 2018, 438: 63-75. DOI: 10.1016/j.canlet.2018.08.030. [5] VAN LIER YF, VOS J, BLOM B, HAZENBERG MD. Allogeneic hematopoietic cell transplantation, the microbiome, and graft-versus-host disease[J]. Gut Microbes, 2023, 15(1): 2178805. DOI: 10.1080/19490976.2023.2178805. [6] LI Y, WANG N, ZHANG X, et al. Post-transplantation cyclophosphamide as GVHD prophylaxis in allogenic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation: recent advances and modification[J]. Blood Rev, 2023, 62: 101078. DOI: 10.1016/j.blre.2023.101078. [7] BOS S, BEECKMANS H, VANSTAPEL A, et al. Pulmonary graft-versus-host disease and chronic lung allograft dysfunction: two sides of the same coin?[J]. Lancet Respir Med, 2022, 10(8): 796-810. DOI: 10.1016/S2213-2600(22)00001-7. [8] ARCHER G, BERGER I, BONDEELLE L, et al. Interstitial lung diseases after hematopoietic stem cell transplantation: new pattern of lung chronic graft-versus-host disease?[J]. Bone Marrow Transplant, 2023, 58(1): 87-93. DOI: 10.1038/s41409-022-01859-4. [9] MOHSENI R, MAHDAVI SHARIF P, BEHFAR M, et al. Evaluation of safety and efficacy of allogeneic adipose tissue-derived mesenchymal stem cells in pediatric bronchiolitis obliterans syndrome (BOS) after allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation (allo-HSCT)[J]. Stem Cell Res Ther, 2023, 14(1): 256. DOI: 10.1186/s13287-023-03498-y. [10] HAKIM A, COOKE KR, PAVLETIC SZ, et al. Diagnosis and treatment of bronchiolitis obliterans syndrome accessible universally[J]. Bone Marrow Transplant, 2019, 54(3): 383-392. DOI: 10.1038/s41409-018-0266-6. [11] GLANVILLE AR, BENDEN C, BERGERON A, et al. Bronchiolitis obliterans syndrome after lung or haematopoietic stem cell transplantation: current management and future directions[J]. ERJ Open Res, 2022, 8(3): 00185-2022. DOI: 10.1183/23120541.00185-2022. [12] HUANG QS, HAN TX, CHEN Q, et al. Clinical risk factors and prognostic model for patients with bronchiolitis obliterans syndrome after hematopoietic stem cell transplantation[J]. Bone Marrow Transplant, 2024, 59(2): 239-246. DOI: 10.1038/s41409-023-02151-9. [13] KWOK WC, LIANG BM, LUI MMS, et al. Rapid versus gradual lung function decline in bronchiolitis obliterans syndrome after haematopoietic stem cell transplantation is associated with survival outcome[J]. Respirology, 2019, 24(5): 459-466. DOI: 10.1111/resp.13472. [14] RHEE CK, HA JH, YOON JH, et al. Risk factor and clinical outcome of bronchiolitis obliterans syndrome after allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation[J]. Yonsei Med J, 2016, 57(2): 365-372. DOI: 10.3349/ymj.2016.57.2.365. [15] MYRDAL OH, AALØKKEN TM, DIEP PP, et al. Late-onset, noninfectious pulmonary complications following allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation: a nationwide cohort study of long-term survivors[J]. Respiration, 2022, 101(6): 544-552. DOI: 10.1159/000520824. [16] FUJII N, NAKASE K, ASAKURA S, et al. Bronchiolitis obliterans with allogeneic hematopoietic cell transplantation: a 10-year experience of the Okayama BMT Group[J]. Int J Hematol, 2014, 99(5): 644-651. DOI: 10.1007/s12185-014-1556-4. [17] YOSHIHARA S, YANIK G, COOKE KR, et al. Bronchiolitis obliterans syndrome (BOS), bronchiolitis obliterans organizing pneumonia (BOOP), and other late-onset noninfectious pulmonary complications following allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation[J]. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant, 2007, 13(7): 749-759. DOI: 10.1016/j.bbmt.2007.05.001. [18] 梁子婷, 许长娟, 曾荣, 等. 9例儿童异基因造血干细胞移植后闭塞性细支气管炎综合征的临床特征[J]. 山东大学学报(医学版), 2022, 60(12): 58-62. DOI: 10.6040/j.issn.1671-7554.0.2022.0386.LIANG ZT, XU CJ, ZENG R, et al. Clinical characteristics of bronchiolitis obliterans syndrome after allogeneichematopoietic stem cell transplantation in 9 children[J]. J Shandong Univ (Health Sci), 2022, 60(12): 58-62. DOI: 10.6040/j.issn.1671-7554.0.2022.0386. [19] AMIN EN, PHILLIPS GS, ELDER P, et al. Health-related quality of life in patients who develop bronchiolitis obliterans syndrome following allo-SCT[J]. Bone Marrow Transplant, 2015, 50(2): 289-295. DOI: 10.1038/bmt.2014.264. [20] DEFILIPP Z, ALOUSI AM, PIDALA JA, et al. Nonrelapse mortality among patients diagnosed with chronic GVHD: an updated analysis from the chronic GVHD consortium[J]. Blood Adv, 2021, 5(20): 4278-4284. DOI: 10.1182/bloodadvances.2021004941. [21] 中国医师协会血液科医师分会, 中华医学会血液学分会. 造血干细胞移植后闭塞性细支气管炎综合征诊断与治疗中国专家共识(2022年版)[J]. 中华血液学杂志, 2022, 43(6): 441-447. DOI: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.0253-2727.2022.06.001.China Hematology Association of Chinese Medical Doctor Association, Chinese Society of Hematology of Chinese Medical Association. Chinese consensus on diagnosis and treatment of bronchiolitis obliterans syndrome after hematopoietic stem cell transplantation (2022)[J]. Chin J Hematol, 2022, 43(6): 441-447. DOI: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.0253-2727.2022.06.001. [22] BANGA A, GILDEA T, RAJESWARAN J, et al. The natural history of lung function after lung transplantation for α(1)-antitrypsin deficiency[J]. Am J Respir Crit Care Med, 2014, 190(3): 274-281. DOI: 10.1164/rccm.201401-0031OC. [23] SHITENBERG D, PERTZOV B, HECHING M, et al. Lung transplantation for graft-versus-host disease after allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation: a single-center experience[J]. Isr Med Assoc J, 2023, 25(3): 227-232. [24] NOGUCHI M, CHEN-YOSHIKAWA TF, ARAI Y, et al. Expanded indications for lung transplantation for pulmonary complications after hematopoietic stem cell transplantation[J]. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg, 2022, 163(4): 1549-1557. DOI: 10.1016/j.jtcvs.2020.10.065. [25] RIDDELL P, VASUDEVAN-NAMPOOTHIRI R, MA J, et al. Lung transplantation for late-onset non-infectious chronic pulmonary complications of allogenic hematopoietic stem cell transplant[J]. Respir Res, 2021, 22(1): 101. DOI: 10.1186/s12931-021-01699-8. [26] TRAUNERO A, PERI F, BADINA L, et al. Hematopoietic stem cells transplant (HSCT)-related chronic pulmonary diseases: an overview[J]. Children (Basel), 2023, 10(9): 1535. DOI: 10.3390/children 10091535. [27] 中华医学会血液学分会造血干细胞应用学组, 中国抗癌协会血液病转化委员会. 慢性移植物抗宿主病(cGVHD)诊断与治疗中国专家共识(2021年版)[J]. 中华血液学杂志, 2021, 42(4): 265-275. DOI: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.0253-2727.2021.04.001.Hematopoietic Stem Cell Application Group, Chinese Society of Hematology, Chinese Medical Association, China Association for the Prevention of Hematology Diseases. Chinese consensus on the diagnosis and management of chronic graft-versus-host disease (2021)[J]. Chin J Hematol, 2021, 42(4): 265-275. DOI: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.0253-2727.2021.04.001. [28] THOMPSON PA, LIM A, PANEK-HUDSON Y, et al. Screening with spirometry is a useful predictor of later development of noninfectious pulmonary syndromes in patients undergoing allogeneic stem cell transplantation[J]. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant, 2014, 20(6): 781-786. DOI: 10.1016/j.bbmt.2014.02.011. [29] BERGERON A, GODET C, CHEVRET S, et al. Bronchiolitis obliterans syndrome after allogeneic hematopoietic SCT: phenotypes and prognosis[J]. Bone Marrow Transplant, 2013, 48(6): 819-824. DOI: 10.1038/bmt.2012.241. [30] AU BK, AU MA, CHIEN JW. Bronchiolitis obliterans syndrome epidemiology after allogeneic hematopoietic cell transplantation[J]. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant, 2011, 17(7): 1072-1078. DOI: 10.1016/j.bbmt.2010.11.018. [31] WADOWSKI B, CHANG SH, CARILLO J, et al. Assessing donor organ quality according to recipient characteristics in lung transplantation[J]. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg, 2023, 165(2): 532-543. DOI: 10.1016/j.jtcvs.2022.03.014. [32] IOAKEIM F, MAZZA T, CASUTT A, et al. When to consider lung transplantation?[J]. Rev Med Suisse, 2022, 18(804): 2143-2149. DOI: 10.53738/REVMED.2022.18.804.2143. [33] NAGATA S, OHSUMI A, HANDA T, et al. Assessment of listing criteria for lung transplant candidates with interstitial lung disease[J]. Gen Thorac Cardiovasc Surg, 2023, 71(1): 20-26. DOI: 10.1007/s11748-022-01861-z. [34] LIAO M, WANG C, ZHANG M, et al. Insight on immune cells in rejection and infection postlung transplant[J]. Immun Inflamm Dis, 2023, 11(7): e868. DOI: 10.1002/iid3.868. [35] FAYYAZ A, RAJA M, NATORI Y. Prevention and management of infections in lung transplant recipients[J]. J Clin Med, 2023, 13(1): 11. DOI: 10.3390/jcm13010011. [36] HOLM AM, RIISE GC, HANSSON L, et al. Lung transplantation for bronchiolitis obliterans syndrome after allo-SCT[J]. Bone Marrow Transplant, 2013, 48(5): 703-707. DOI: 10.1038/bmt.2012.197. [37] OLIVEROS MJ, SERON P, ROMÁN C, et al. Two-minute step test as a complement to six-minute walk test in subjects with treated coronary artery disease[J]. Front Cardiovasc Med, 2022, 9: 848589. DOI: 10.3389/fcvm.2022.848589. [38] GUPTA R, BAUGHMAN RP, NATHAN SD, et al. The six-minute walk test in sarcoidosis associated pulmonary hypertension: results from an international registry[J]. Respir Med, 2022, 196: 106801. DOI: 10.1016/j.rmed.2022.106801. -





 下载:
下载: